

How Freeze-Drying Works
Freeze-drying food is an innovative preservation method. It allows for long-term storage while retaining nutritional value and flavor.
But how freeze-drying works might surprise you. This process involves removing moisture from food through a unique method.
In this article, we will explore the science behind freeze-drying. Get ready to discover the intricate steps involved in this fascinating technology.
Understanding Freeze-Drying
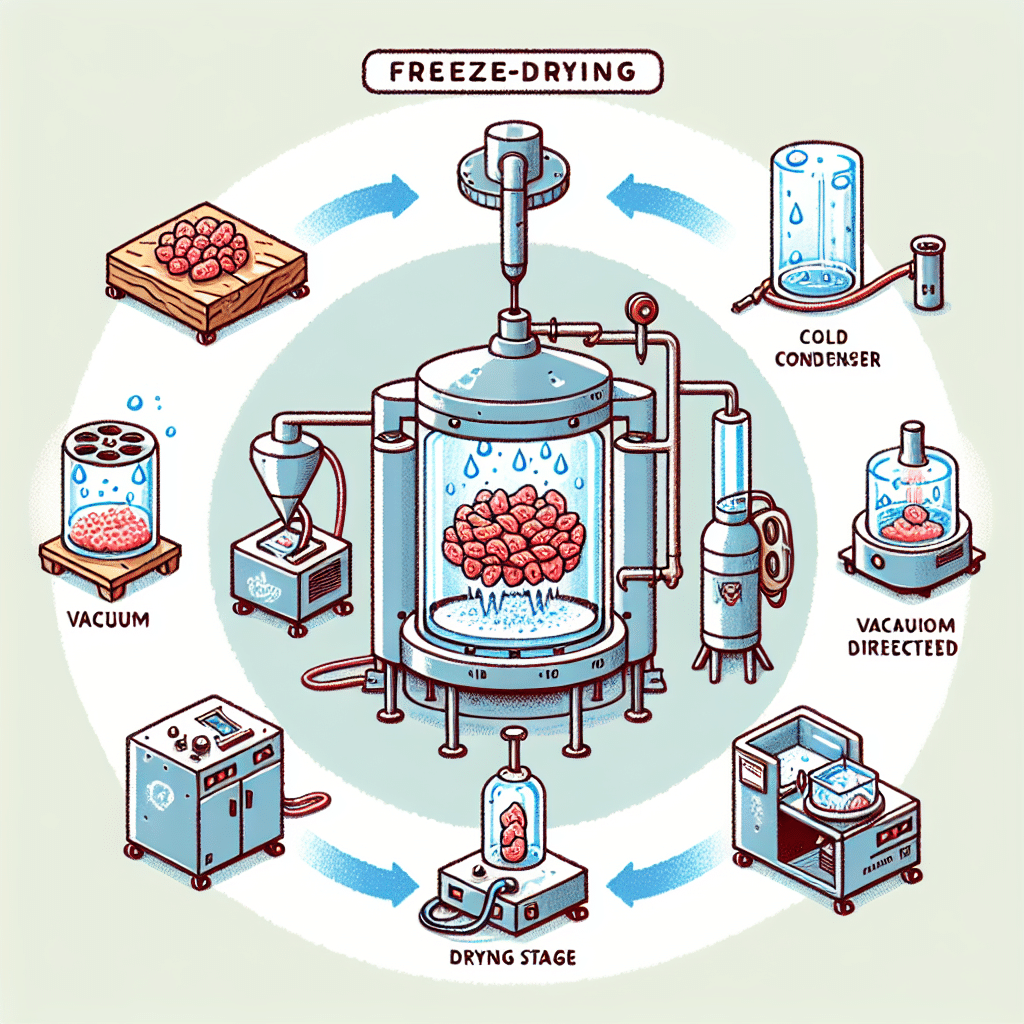
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a method of preserving food that involves removing its water content.
This process is achieved by freezing the food and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water in the food to sublimate directly from the solid phase to the gas phase.
The Basics of Freeze-Drying
The freeze-drying process is carried out in a machine called a freeze-dryer.
This appliance consists of a vacuum chamber, a condenser, and a refrigeration system.
The Science Behind Sublimation
Sublimation is a fascinating scientific phenomenon.
It’s the transition of a substance directly from a solid state, like ice, to a gas state, skipping the liquid phase entirely. This is the core principle that makes freeze-drying possible.
The Freeze-Drying Process
The freeze-drying process is a meticulous one, involving three main stages: pre-freezing, primary drying (sublimation), and secondary drying (desorption).
Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and longevity of the freeze-dried food.
Pre-Freezing Stage
The pre-freezing stage involves freezing the food to a temperature below its triple point.
This ensures that sublimation, rather than melting, occurs in the following stage.
Primary Drying (Sublimation) Stage
In the primary drying stage, the pressure is reduced and heat is added to encourage sublimation.
This means the ice in the food directly converts into water vapor, leaving the food dry.
Secondary Drying (Adsorption) Stage
The secondary drying stage aims to remove any unfrozen water molecules.
The temperature is raised higher than in the primary drying stage, and this helps to remove water molecules that are bound to the food.
Benefits of Freeze-Drying Food
Freeze-drying food offers numerous benefits, making it a popular choice for preservation.
From nutritional preservation to extended shelf life, the advantages are significant.
Nutritional Preservation
One of the key benefits of freeze-drying is the preservation of nutrients.
Unlike other methods, freeze-drying maintains the nutritional content of the food, ensuring you get the most out of your meals.
Shelf Life and Storage
Freeze-dried foods boast an impressive shelf life, often ranging from 25 to 30 years when properly sealed.
This makes them ideal for long-term storage, emergency preparedness, and reducing food waste.
Home Freeze-Drying: Practical Uses and Tips
Freeze-drying at home opens up a world of culinary possibilities.
From preserving seasonal produce to creating unique dishes, the applications are vast and varied.
Incorporating Freeze-Dried Ingredients in Cooking
Freeze-dried ingredients can add a new dimension to your cooking.
They provide intense flavor without additional moisture, making them perfect for a variety of recipes.
Selecting and Operating a Home Freeze-Dryer
Choosing the right freeze-dryer for your needs is crucial.
Consider factors like capacity, ease of use, and the ability to control temperature for efficient operation.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While freeze-drying offers many benefits, it’s important to consider potential drawbacks.
These include the initial cost of the appliance and the space it requires in your kitchen.
Cost and Energy Consumption
Freeze-drying can be energy-intensive, which may increase your utility bills.
Also, home freeze-dryers, while smaller than commercial units, can still be a significant investment.
Conclusion: Is Freeze-Drying Right for You?
Understanding how freeze-drying works can help you decide if it’s right for your kitchen. Consider the benefits, drawbacks, and your personal cooking goals. With the right knowledge, you can make an informed decision and potentially add a new dimension to your culinary creations.

